2. Digits
Find the number of digits in a
nonnegative integer n.
Input. One
nonnegative integer n (0 ≤ n ≤ 2*109).
Output. The
number of digits in number n.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
13243 |
5 |
SOLUTION
elementary
problem
Algorithm
analysis
The number of digits in a number can
be found:
·
using one loop.
·
in recursive way, using the recurrence relation:
digits(n) = 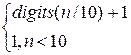
Algorithm
realization
Read the input value n. If n =
0, the answer is 1. Otherwise initialize res
with 0 and compute the number of digits in n
using a while loop.
scanf("%d",&n);
res = (n == 0);
while(n > 0)
{
n /= 10;
res++;
}
printf("%d\n",res);
Algorithm realization – recursive
#include <stdio.h>
int n, res;
int digits(int n)
{
if (n < 10) return
1;
return 1 + digits(n / 10);
}
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
res =
digits(n);
printf("%d\n",res);
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int digits(int n)
{
if (n < 10) return 1;
return 1 + digits(n / 10);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new
Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int res = digits(n);
System.out.println(res);
con.close();
}
}
Python realization
Convert
the input number n to a string, and then find its length.
n = int(input())
print(len(str(n)))
If there are spaces before
the number, then the following implementation will fail:
s = str(input())
print(len(s))
Implementation
with while loop:
x = int(input())
cnt = 0
if x == 0:
print ("1")
else:
while x > 0:
cnt += 1
x = x // 10
print (cnt)
Python realization – recursion
def f(n):
if n < 10:
return 1
return f(n / 10) + 1
n = int(input())
print (f(n))